Open Access

Subscription Access
Morin augmented the metabolism and detoxification of ethanol: effects on TGF-β and the collagen accumulation
Anbu Singaravelu, Niyas Ahamed Md Iqbal, Padma Jayabalan, Saravanan Nadanam
Abstract
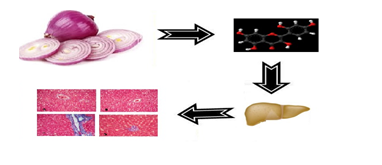
The present study was conducted to evaluate the effects of morin on the metabolism and detoxification of ethanol in the liver fibrosis. Male albino Wistar rats were divided into four groups as follows: Group 1 rats received isocaloric glucose every day, Group 2 rats received morin (60 mg/kg BW/day) everyday during the post 30 days of the experimental period; Group3received ethanol (6 g/kg BW/day) everyday for 60days, Group 4 ethanol fed rats treated with morin (60 mg/kg BW/day) for post 30 days. Ethanol treated rats showed increased levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), free fatty acids (FFA), Phospholipids (PL), activities of phase I enzymes, transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), decrease in alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) and phase II enzymes. Liver fibrosis in the ethanol-fed rats as evidence by Masson's Trichrome staining. Ethanol fed rats treated with morin significant normalize the levels/activities of lipids, phase I enzymes, ADH, ALDH, phase II enzymes, TGF-β1 and collagen in liver. Thus morin curtail ethanol induced liver fibrosis and the results were supported with In vitro antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of morin.
Keywords
Ethanol; liver fibrosis; morin; transforming growth factor; Masson'strichrome
Full Text:
PDF

ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825