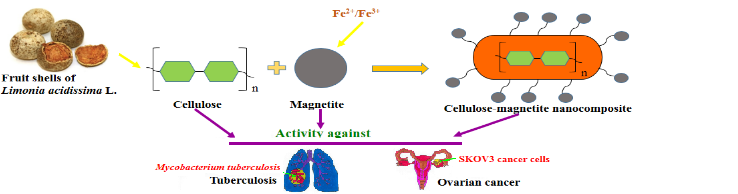
In vitro anticancer and antitubercular activities of cellulose-magnetite nanocomposite synthesized using deep eutectic solvent as a dispersant
Abstract
In the current scenario, DESs are persuasive greener solvents for the successful synthesis of different nanostructures due to their tunable properties with enhanced applications. We report here the successful formation of a nanocomposite based on cellulose and magnetite nanoparticles. The method of isolating cellulose from fruit shells of Limonia acidissima (L.) as detailed in the work is described for the first time to the best of our knowledge. Magnetite nanoparticles are synthesized through the cost effective co-precipitation method and DES embracing choline chloride and fructose is used as a non-toxic dispersant for the synthesis of cellulose-magnetite nanocomposite. Various physiochemical parameters like compositional, structural, morphological and magnetic properties are analyzed using FTIR, XRD, HRTEM, SAED and VSM techniques. Anticancer and antitubercular activities, performed by MTT and LRP assays respectively, reveals that the IC50 values for cellulose, magnetite and cellulose-magnetite nanocomposite are found to be 20.65 µg/ml, 44.66 µg/ml and 8.685 µg/ml and cellulose-magnetite nanocomposite shows 51.95% inhibition at 200 µg/ml concentration against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The obtained results suggest that the prepared cellulose-magnetite nanocomposite can serve as a potential candidate for drug designing with the use of green solvents.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFRefbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
ISSN 2394-0867
 ISSN 2394-0867
ISSN 2394-0867