Role of Epigenetic changes in Reproductive Inflammation and Male Infertility
Abstract
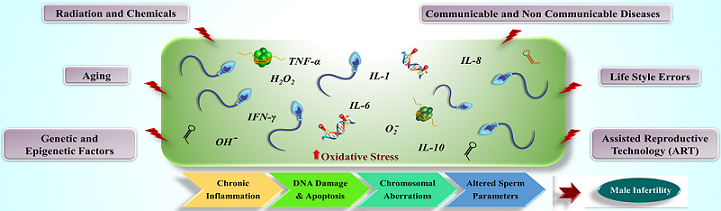
Male infertility is a public health problem affecting one in twenty couples globally. This multifactorial reproductive health issue is a consequence of testicular failure, ejaculatory dysfunction, and altered sperm characteristics caused by a combination of (epi) genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Aberrations in epigenetic changes have been proposed as an important causative factor for infertility in men. Abnormal DNA methylation, histone modification, altered non-coding RNAs have been well documented as in pathological conditions such as oligospermia, azoospermia, asthenospermia and tetratospermia in males. Additionally, chronic inflammations in the male genital tract have long been linked with infertility, possibly via affecting the sperm epigenome or its surrounding microenvironment. This review article summarizes the relationship between epigenome, inflammation, and its contribution to male infertility.
Keywords
ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825