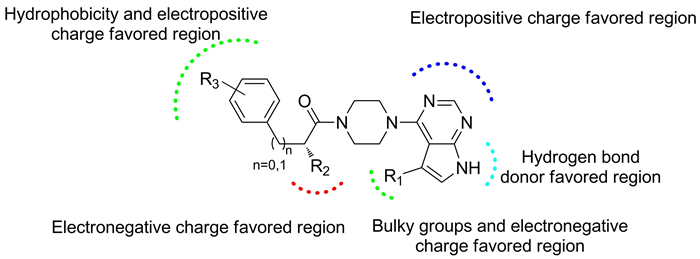
3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies of ATP-competitive Akt inhibitors with the scaffold 4-(piperazin-1-yl)pyrimidine
Abstract
Keywords
References
P.F. Jones, T. Jakubowicz, F.J. Pitossi, F. Maurer, B.A. Hemmings. Molecular cloning and identification of a serine/threonine protein kinase of the second-messenger subfamily. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1991, 88, 4171-4175.
A. Bellacosa, J.R. Testa, S.P. Staal, P.N. Tsichlis. A Retroviral Oncogene, akt, Encoding a Serine-Threonine Kinase Containing an SH2-Like Region. Science 1991, 254 (5029), 274-277.
P.J. Coffer, J.R. Woodgett. Molecular cloning and characterisation of a novel putative protein-serine kinase related to the cAMP-dependent and protein kinase C families. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 201, 475-481.
M. Hanada, J.H. Feng, B.A. Hemmings. Structure, regulation and function of PKB/AKT—a major therapeutic target. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Proteins Proteomics 2004, 1697 (2004), 3-16.
H.G. Wendel, E.de Stanchina, J.S. Fridman, A. Malina, S. Ray, S. Kogan, C. Cordon-Cardo, J. Pelletier, S.W. Lowe. Survival signalling by Akt and eIF4E in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nature 2004, 428 (6980), 332-337.
L.R. Pearce, D. Komander, D.R. Alessi. The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11 (1), 9-22.
I. Vivanco, C.L. Sawyers. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–Akt pathway in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2 (7), 489-501.
P.J. Coffer, J. Jin, J.R. Woodgett. Protein kinase B (c-Akt) : a multifunctional mediator of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. Biochem. J. 1998, 335 (1), 1-13.
E. Barile, S.K. De, C.B. Carlson, V. Chen, C. Knutzen, M. Riel-Mehan, L. Yang, R. Dahl, G. Chiang, M. Pellecchia. Design, Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationships of 3-Ethynyl-1H-indazoles as Inhibitors of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signaling Pathway. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8368-8375.
Y.O. Al-Bazz, J.C.E. Underwood, B.L. Brown, P.R.M. Dobson. Prognostic signiï¬cance of Akt, phospho-Akt and BAD expression in primary breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 694-704.
V. Shtilbans, M.X. Wu, D.E. Burstein. Current overview of the role of Akt in cancer studies via applied immunohistochemistry. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2008, 12, 153-160.
K. Lin, J. Lin, W.I. Wu, J. Ballard, B.B. Lee, S.L. Gloor, G.P.A. Vigers, T.H. Morales, L.H. Friedman, N. Skelton. An ATP-Site On-Off Switch That Restricts Phosphatase Accessibility of Akt. Sci. Signaling 2012, 5 (223), 1-10.
C.S. Mitsiades, N. Mitsiades, M. Koutsilieris. The Akt Pathway: Molecular Targets for Anti-Cancer Drug Development. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2004, 4, 235-256.
D.A. Altomare, J.R. Testa. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7455-7464.
A. Bellacosa, C.C. Kumar, A. Di Cristofano, J.R. Testa. In Advances in Cancer Research; G.F. VandeWoude, G. Klein; Elsevier: San Diego, 2005; Vol.94, pp 29–86.
P. Wang, L. Zhang, Q. Hao, G. Zhao. Developments in Selective Small Molecule ATP-Competitive Inhibitors Targeting the Serine/Threonine Kinase Akt/PKB. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1093-1107.
Q. Hao, Y. Zhong, P. Wang, G.S. Zhao. Research progress of protein kinase B/Akt inhibitors. Chemistry of Life 2011, 31 (4), 557-565.
C.W. Lindsley, Z.J. Zhao, W.H. Leister, R.G. Robinson, S.F. Barnett, D. Defeo-Jones, R.E. Jones, G.D. Hartman, J.R. Huff, H.E. Huber, M.E. Duggan. Allosteric Akt (PKB) inhibitors: discovery and SAR of isozyme selective inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 761-764.
G. Saxty, S.J. Woodhead, V. Berdini, T.G. Davies, M.L. Verdonk, P.G. Wyatt, R.G. Boyle, D. Barford, R. Downham, M.D. Garrett, R.A. Carr. Identification of Inhibitors of Protein Kinase B Using Fragment-Based Lead Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2293-2296.
K.D. Freeman-Cook, C. Autry, G. Borzillo, D. Gordon, E. Barbacci-Tobin, V. Bernardo, D. Briere, T. Clark, M. Corbett, J. Jakubczak, S. Kakar, E. Knauth, B. Lippa, M.J. Luzzio, M. Mansour, G. Martinelli, M. Marx, K. Nelson, J. Pandit, F. Rajamohan, S. Robinson, C. Subramanyam, L.Q. Wei, M. Wythes, J. Morris. Design of Selective, ATP-Competitive Inhibitors of Akt. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4615-4622.
S.H. Chang, Z. Zhang, X.X. Zhuang, J.F. Luo, X.W. Cao, H.L. Li, Z.C. Tu, X.Y. Lu, X.M. Ren, K. Ding. New thiazole carboxamides as potent inhibitors of Akt kinases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1208-1212.
M. Addie, P. Ballard, D. Buttar, C. Crafter, G. Currie, B.R. Davies, J. Debreczeni, H. Dry, P. Dudley, R. Greenwood, P.D. Johnson, J.G. Kettle, C. Lane, G. Lamont, A. Leach, R.W.A. Luke, J. Morris, D. Ogilvie, K. Page, M. Pass, S. Pearson, L. Ruston. Discovery of 4‑Amino‑N‑[(1S)‑1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]- 1-(7H‑pyrrolo[2,3‑d]pyrimidin-4-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamide (AZD5363), an Orally Bioavailable, Potent Inhibitor of Akt Kinases. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2059-2073.
J.F. Blake, N.C. Kallan, D.M. Xiao, R. Xu, J.R. Bencsik, N.J. Skelton, K.L. Spencer, I.S. Mitchell, R.D. Woessner, S.L. Gloor, T. Risom, S.D. Gross, M. Martinson, T.H. Morales, G.P.A. Vigers, B.J. Brandhuber. Discovery of pyrrolopyrimidine inhibitors of Akt. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5607-5612.
Clinical information can be found at www.clinicaltrials.gov by entering following identifiers: NCT01090960, NCT01353781, NCT00920257, NCT01532700, NCT01283035.
J. Fang, D. Huang, W. Zhao, H. Ge, H.B. Luo, J. Xu. A New Protocol for Predicting Novel GSK-3β ATP Competitive Inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 1431-1438.
V.K. Vyas, N. Gupta, M. Ghate. CoMFA and CoMSIA analysis of protein kinase B (PKBβ) inhibitors using various alignment methods. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 6046–6062.
V.K. Vyas, M. Ghate, N. Gupta. 3D QSAR and HQSAR analysis of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) inhibitors using various alignment methods. Arabian J. Chem. 2013.
M. Muddassar, F.A. Pasha, M.M. Neaz, Y. Saleem, S.J. Cho. Elucidation of binding mode and three dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship studies of a novel series of protein kinase B/Akt inhibitors. J. Mol. Model. 2009, 15, 183-192.
R.D. Cramer, D.E. Patterson, J.D. Bunce. Comparative Molecular Field Analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of Shape on Binding of Steroids to Carrier Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 5959-5967.
G. Klebe, U. Abraham, T. Mietzner. Molecular Similarity Indices in a Comparative Analysis (CoMSIA) of Drug Molecules To Correlate and Predict Their Biological Activity. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 4130-4146.
G. Klebe. Perspectives in Drug Discovery and Design, Kluwer Academic Publishers: Great Britain, 1998.
M. Clark, R.D. Cramer, N. Van Opdenbosch. Validation of the General Purpose Tripos 5.2 Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 982-1012.
Cho, S. J.; Tropsha, A. Cross-Validated R2-Guided Region Selection for Comparative Molecular Field Analysis: A Simple Method To Achieve Consistent Results. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 1060.
S.Yu, P. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Liu, G. Zhao. Docking-based CoMFA and CoMSIA study of azaindole carboxylic acid derivatives as promising HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2013, 24, 819-839.
B.L. Bush, B. Robert, Jr. Nachbar. Sample-distance Partial Least Squares: PLS optimized for many variables, with application to CoMFA. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 1993, 7, 587-619.
D.T. Manallack, D.D. Ellis, D.J. Livingstone. Analysis of Linear and Nonlinear QSAR Data Using Neural Networks. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 3758-3767.
R.X. Wang, Y.P. Lu, S.M. Wang. Comparative Evaluation of 11 Scoring Functions for Molecular Docking. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2287-2303.
J.F. Blake, R. Xu, J.R. Bencsik, D. Xiao, N.C. Kallan, S. Schlachter, I.S. Mitchell, K.L. Spencer, A.L. Banka, E.M. Wallace, S.L. Gloor, M. Martinson, R.D. Woessner, G.P.A. Vigers, B.J. Brandhuber, J. Liang, B.S. Safina, J. Li, B. Zhang, C. Chabot, S. Do, L. Lee, J. Oeh, D. Sampath, B.B. Lee, K. Lin, B.M. Liederer, N.J. Skelton. Discovery and Preclinical Pharmacology of a Selective ATP-Competitive Akt Inhibitor (GDC-0068) for the Treatment of Human Tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55 (18), 8110-8127.
ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825