Role of estrogens in immunoendocrine regulations of male reproduction
Debosree Ghosh, Alak Kumar Syamal, Suvendu Ghosh
Abstract
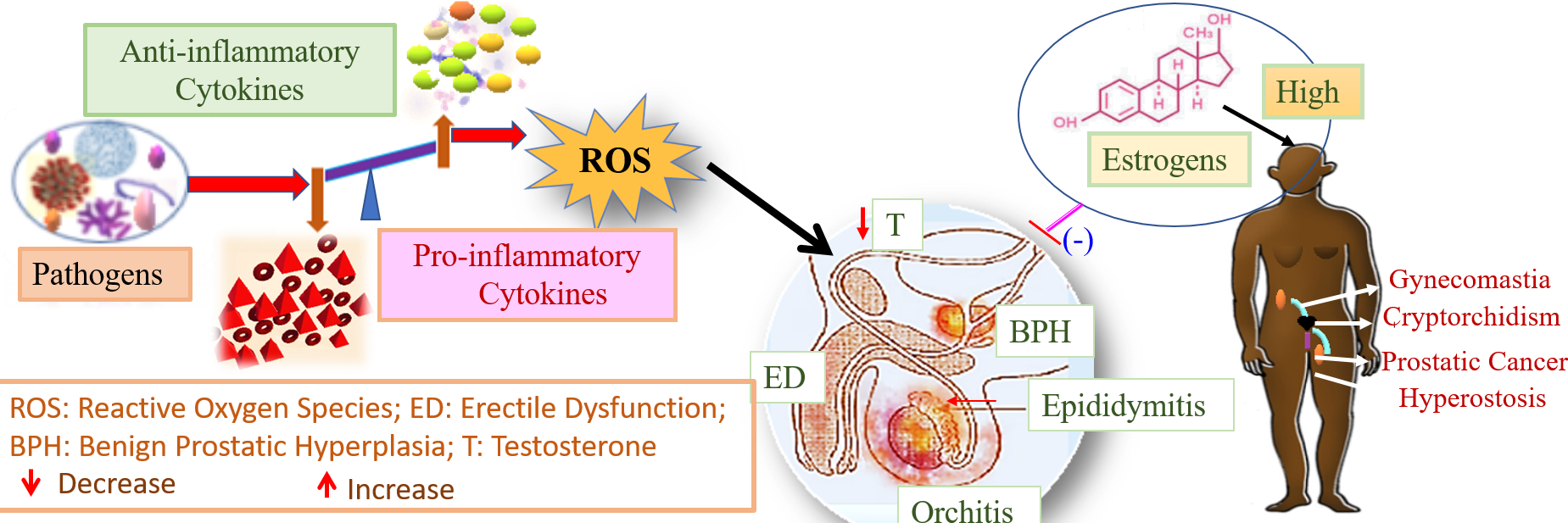
Male infertility is a multifactorial disorder. A diverge array of autocrine and paracrine factors, genetic and epigenetic factors, pathogenic perturbations, testicular dysfunctions and oxidative stress, all together may contribute to male infertility. Interactions between different cellular components of testis, other accessory sex organs and hormones within the system’s milieu act in a synchronized manner to help in normal reproductive function. In addition, immune cells and hormonal interplay may also assist such mechanisms. Androgens and estrogens are known to act as antagonizing hormones. They act via multiple receptors mediated signaling, producing such effects. Nevertheless, recent cropping up evidences in support of the role of hormones in managing testicular function indicate a vital role of estrogenic influences. Dietary or occupational exposure to artificial or natural estrogen may act as teratogen and a factor for some secular diseases of male reproductive tract leading to immune endocrine disbalances contributing to male infertility. The key role of estrogen in immune modulation related to immune dysfunction and inflammatory conditions in male germ cell signaling, Sertoli cell integrity and expression of altered immune responses are of a matter of great concern. Suppression of autoreactive immune cells, alterations of regulatory T cells (T Reg), Th1 and Th2 ratio, Th17 cell responses, manipulation of inflammatory and autoimmune response confirms the essential role of estrogen in promoting protection against inflammatory conditions. Nevertheless, evidence based extensive research is essential to overrule the possibility of adverse outcomes of this sex steroid and sustain its beneficial action of estrogen in males.
Keywords
Hypogonadism; male infertility; Sertoli cells; Immune modulation; breast cancer, prostrate
ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825