Obesity and Male Infertility: Energy Imbalance to Inflammation
Mehmet Murad Basar, A. Egemen Avci
Abstract
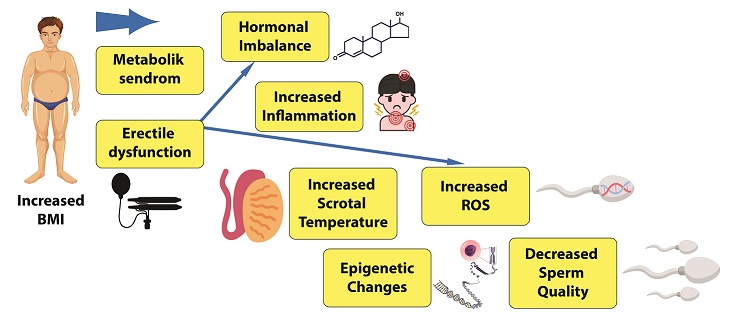
Obesity is an important health problem with an increasing frequency in the world. In recent years, obesity has been shown to be closely related to infertility in addition to causing many important additional and systemic health problems. The relationship between obesity and infertility is evaluated based on many complex mechanisms, such as inflammatory cellular response, endocrine factors released from adipose tissue, and epigenetic changes, as well as other known factors including increased scrotal temperature and hormonal imbalance. While increasing BMI negatively affects the known reproductive hormonal mechanism, on the other hand, adipose tissue acts as an endocrine organ and secretes several hormones called adipokines. These hormones affect spermatogenesis both central and testicular ways. Moreover, increased adipose tissue and BMI cause to rising scrotal temperature, and result in sperm DNA damage. Therefore, sperm DNA damage caused by both the negative effect of adipokines, increased scrotal temperature, and increased inflammatory response impairs sperm functional structure. In addition to all these factors, sexual dysfunction which develops due to hormonal imbalance as a result of excess weight and psychologic factors caused by a distorted body image, constitute an important obstacle to a healthy sexual life. As a result, obesity should be considered as a health problem that plays a role in male infertility with its multi-faceted interaction.
Keywords
adipose tissue; male infertility; obesity; oxidative damage
ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825