Leptin in Energy homeostasis, Male reproduction, and Immune regulation
Abstract
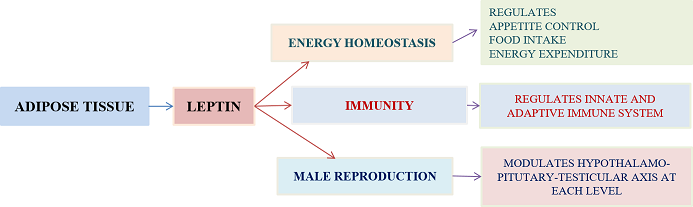
Discovery of leptin has changed the view of adipose tissue from energy storehouse to a active neuroendocrine and immune organ Adipokine leptinis a16 kDa amino acid protein,encoded by LEP gene, secreted by adipose tissue, and acts through its cytokine receptor leptin receptor. Leptin is a central regulator of energy homeostasis by regulating food intake, appetite, satiety and basal metabolism. Leptin acts at each level of hypothalamus pituitary gonadal axis (HPG) and has a key role in initiation and progression of pubertal events and sexual maturation. Leptin acts directly at testicular level and affects the spermatogenesis, sperm quality and capacitation thus has important role in male reproduction and fertility. Leptin receptors are present on every cells involved in innate and adaptive immunity and regulate the functions of these cells. Leptin has been implicated in pathogenesis of multiple disorders like obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, SLE, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, male infertility and other chronic inflammatory disorders due to its varied actions on different organ systems. Therapies based on modulating the functions of leptin can be the key area of research in future for treatment of these chronic disorders.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825