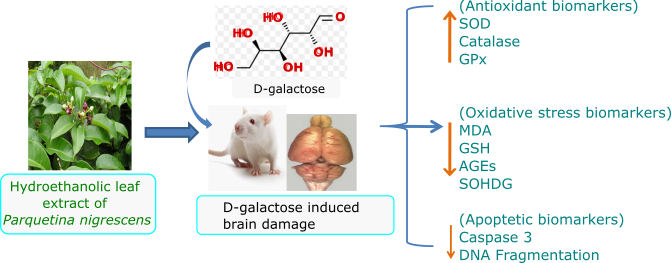
Protective effect of hydroethanolic leaf extract of Parquetina nigrescens against D-galactose-induced neurotoxicity in male Wistar rats.
Abstract
 To investigate the effect of hydroethanolic leaf extract of Parquetina nigrescens (HELEPN) on D-galactose induced neurotoxicity in male Wistar rats.Brain damage was induced by the administration of 300mg/kg b.w of D-galactose subcutaneously for six weeks while HELEPN treatments (250mg and 500 mg/kg b.w) were given orally for four weeks. After the study, rats were sacrificed and brain tissues collected for biochemical analysis. The concentrations of Advanced GlycationEndproducts (AGEs), Tumour Necrosis Factor α (TNF-α), 8-dehydroyxguanosine (8-OHDG) and Caspase 3 activity were done using Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. Levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione, Nitric oxide and activities of Acetycholinestrease (AChE), Superoxide dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT), Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) as well as DNA fragmentation index (DFI) were determined using standard techniques. HELEPN administration attenuated D-galactose-induced brain alterations through decreased MDA level and increased activities of SOD, CAT as well as elevated glutathione content. HELEPN also improved the activities of brain caspase 3-dependent apoptosis and AChE, TNF-α and DNA fragmentation index.The administration of HELEPN provided neuroprotection against D-galactose-induced brain damage through anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory as well as anti-apoptotic mechanisms and these protective effects could be as a result of a profile of phytochemicals present in the plant leaves.
Keywords
ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825